- HOME
- Primary Sources
- The Invention of the Sewing Machine by Grace Rogers Cooper
- The Sewing Machine Combination or Sewing Machine Trust
- Vibrating Shuttle Sewing Machines History
- Running-Stitch Machines
- Button-Hole Machines
- Book-Sewing Machines
- Glove-Sewing Machines
- Shoe Making Machines
- Needles
- Shuttles & Bobbins
- Bobbin Winders
- Thread Tension Regulators
- Feed Reversing Mechanism
- Attachments and Accessories
- MANUFACTURERS AND DEALERS IN SEWING MACHINES
- BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCHES
- PATENTS
- DATING FRISTER & ROSSMANN
- FRISTER & ROSSMANN
- BRITISH Machines
- BRITISH Machines Part 1
- BRITISH Machines Part 2
- BRADBURY & Co.
- BRITANNIA SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- BRITISH SEWING MACHINE COMPANY Ltd
- ECLIPSE MACHINE COMPANY
- ESSEX
- GRAIN E. L. Ltd
- W. J. HARRIS & C0.
- IMPERIAL SEWING MACHINE CO.
- JONES & CO.
- LANCASHIRE SEWING MACHINE Co
- SELLERS W.
- SHEPHERD, ROTHWELL & HOUGH
- VICKERS
- WEIR'S
- AMERICAN Machines
- AETNA SEWING MACHINE
- AMERICAN B.H.O. & SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- AMERICAN SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- AVERY SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- BARTHOLF SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- BARTLETT SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- BARTRAM & FANTON Mfg. Co.
- BECKWITH SEWING MACHINE Co.
- BOYE NEEDLE COMPANY
- BURNET, BRODERICK & CO.
- CONTINENTAL MANUFACTURING Co.
- DAVIS SEWING MACHINE CO.
- DEMOREST SEWING MACHINE MANUFACTURING CO.
- DOMESTIC SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- DORCAS Sewing Machine
- EMPIRE SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- EPPLER & ADAMS SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- GOODSPEED & WYMAN S.M. Co.
- GREIST MANUFACTURING COMPANY
- GROVER & BAKER SMC
- HEBERLING RUNNING STITCH GUAGING MACHINE Co.
- HIBBARD, SPENCER, BARTLETT & Co.
- HODGKINS MACHINE
- HOWE MACHINE COMPANY (Elias)
- HOWE S. M. C. (Amas)
- N. HUNT & CO.
- HUNT & WEBSTER
- JOHNSON, CLARK & CO.
- LEAVITT & CO.
- LEAVITT SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- LEAVITT & BRANT
- LENOX MANUFACTURING COMPANY
- NETTLETON & RAYMOND SEWING MACHINES
- NEW HOME SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- NICHOLS & BLISS
- NICHOLS & Co.
- NICHOLS, LEAVITT & CO.
- REMINGTON SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- REECE BUTTON HOLE MACHINE COMPANY
- SINGER
- SMYTH MANUFACTURING COMPANY
- UNION BUTTONHOLE and EMBROIDERY MACHINE COMPANY
- UNION BUTTON-HOLE MACHINE COMPANY
- UNION BUTTON SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- TABITHA Sewing Machine
- WARDWELL MANUFACTURING COMPANY
- WATSON, WOOSTER & Co.
- WEED SMC
- WHEELER & WILSON
- WHITE SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- WILLCOX & GIBBS
- WILSON SEWING MACHINE COMPANY
- CANADIAN Machines
- GERMAN Machines
- Deutsche Nähmaschinen-Hersteller und Händler
- Development in industrial sales
- About innovations on sewing machines
- Bielefeld Nähmaschinenfabriken
- Nähmaschinen in Leipzig
- ADLER
- ANKER-WERKE A.G.
- BAER & REMPEL
- BEERMANN CARL
- BELLMANN E.
- BIESOLT & LOCKE
- BOECKE
- BREMER & BRÜCKMANN
- CLAES & FLENTJE
- DIETRICH & Co.
- DÜRKOPP
- GRIMME, NATALIS & Co.
- GRITZNER
- HAID & NEU
- HENGSTENBERG & Co.
- JUNKER & RUH
- KAISER
- LOEWE & Co. / LÖWE & Co.
- MANSFELD
- MÜLLER CLEMENS
- MUNDLOS
- OPEL
- PFAFF
- POLLACK , SCHMIDT & CO.
- SCHMIDT & HENGSTENBERG
- SEIDEL & NAUMANN
- SINGER NÄHMASCHINEN IN GERMANY
- STOEWER
- VESTA
- WERTHEIM
- WINSELMANN
- ITALIAN Machines
- HUNGARIAN / MAGYAR Machines / Varrógépek
- AUSTRIAN Machines
- BELGIAN Machines
- FRENCH Machines
- RUSSIAN Machines
- SWEDISH Machines
- SWISS Machines
- NATIONAL & INTERNATIONAL EXHIBITIONS
- 1850 NEW YORK - FAIR
- 1850 BOSTON
- 1851 LONDON
- 1851 NEW YORK - FAIR
- 1852 NEW YORK - FAIR
- 1853 NEW YORK - FAIR
- 1853 BOSTON
- 1853 DUBLIN
- 1853-4 NEW YORK
- 1854 MELBOURNE
- 1855 NEW YORK - FAIR
- 1855 PARIS
- 1856 BOSTON
- 1856 NEW YORK - FAIR
- 1860 STUTTGART
- 1861 MELBOURNE
- 1862 LONDON
- 1866 ALTONA
- 1869 BOSTON
- 1873 VIENNA World Exhibition
- 1876 PHILADELPHIA
- 1884 LONDON Health Exhibition
- 1884 LONDON International and Universal Exhibition
- 1885 LONDON South Kensington Exhibition
- 1887 LONDON American Exhibition
- 1889 PARIS Exposition Universelle
- 1893 LONDON The Sewing and Domestic Machines' Show
- CURIOSITIES
- READING ROOM
- SEWING MACHINE MUSEUMS - Links
- USEFUL LINKS
BRITISH PATENTS
1617 - 1852 (Old Series)
Chronological List of British Patent Models
Until 1852 patents (covering England and Wales only) were obtained through the complex medieval system which required visiting seven different offices and two signatures by the monarch. Patents granted under this system were not numbered and not published by the authorities at that time (though the details of some were printed in journals such as the Repertory of Arts). Following the modernisation of the patent law in 1852, 14.359 patents granted up to that date were given numbers of the form No nnnn/yyyy, eg No 1/1617, No 913/1769 and published during the 1850s
-----------------------------------------------------------------
First Patent
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Aaron Rapburne & Roger Burges
GB 1 (March 2, 1617)
A privilege granted to Aaron Rapburne, gent., & Roger Burges, for terme of XXI years next, of the sole making, describing, carving & graving in copper, brasse, or other metall, all such and soe manie mappes, plotts or descriptions of Lond. Westm. Bristol, Norwich, Canterbury, Bath, Oxford & Cambridge and the towne & castle of Windsor, & to imprint and sett forth & sell the same.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 515/1730 John Kay
Engine for making, twisting and cording mohair and worsted, also twining and dressing thread for tailors and others
May 8, 1730
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 542/1733 John Kay
A new invention of a shuttle for the better and more exact weaving of broad cloths, broad bays, sail cloths
May 26, 1733
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 701/1755 Charles Frederick Wiesenthal
A new invented art of working fine thread in needlework after the manner of Dresden needlework
June 24, 1755
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 955/1770 Robert Alsop
An invention of a new species of embroidery for clothes
Weaving embroidered stuffs in a loom, with one, two or more shuttles. Printed, 4d. No Drawings.
March 22, 1770
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 1.097/1775 William Sheward
A new invented method of making needles, with the eyes thereof upon a new and particular construction
June 10, 1775
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Making and completing shoes, boots, spatterdashes, clogs and other articles, by means of tools or machines for the purpose
July 17, 1780
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 2.769/1804 John Duncan
Improved method or means of tambouring or raising of flowers, figures, or other ornaments upon muslins, lawns and other cottons, cloths, or stuffs, or upon silk, linen, or woollen cloths or stuffs, or upon cloths or stuffs composed partly of silk, flax, cotton, or woollen
Machinery for tambouring upon cloth, by which one person is enabled to work with a large number of barbed needles or hooks at the same time, instead of employing only one needle or hook, as when tambouring solely by manual labour. The barbed ends of all the needles pass simultaneously through the cloth; then each needle is supplied with thread by a feeding needle, which passes the thread around the tambouring needle and under the barb thereof and when the tambouring needle recedes, it drawn by it through the cloth. These movements are repeated until the pattern is complete and when this is the case, the machinery is worked in a suitable manner to secure the ends of the threads. The pattern (which will consist of a number of similar figures) may be produced by moving the needles horizontally or vertically at the requisite times in front of the cloth, or by moving the cloth in front of the needles or hooks. The latter plan is preferred by the patentee and is effected as follows: The cloth is stretched in a vertical position between two cylinders placed parallel to each other in an oblong frame and the latter slides freely to and fro horizontally carrying the first frame with it. Thus, either a vertical or horizontal motion may be communicated to the cloth and when both are communicated at the same time, the cloth moves in an oblique direction. By these means, every rectilinear or curvilinear figure may be produced and consequently, every pattern required. Printed, 5s. Drawings.
May 30, 1804
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 3.012/1807 James Winter
Machine for sewing, &c, leather gloves
Apparatus to be used for sewing and pointing leather gloves, consisting of a pedestal supporting a pair of jaws, which receive the leather to be sewed or ornamented, together with an instrument termed an "index", formed with grooves on the top or face to guide the needles. One jaw is capable of turning on a joint and is kept closed by a spring during the operation of sewing; it is opened, when required, by placing the foot on a treadle connected by a cord with a pin projecting from such moveable jaw. The index may be made of ivory, bone, brass or any other fit material and consists of two pieces or sides, either straight or curved, according to the part of glove to be sewed and capable of adjustment with regard to each other by means of a screw, so that the grooves on the top of the two sides may be made to correspond. In sewing, the needles are passed through the grooves in the index, which must be made of the depth required for the stitch, the leather being placed even with face or top of the index.The grooves in the index may be varied, so that the different kinds of sewing and ornamental work may be performed with one, two three or four needles and for single and double seaming, the index may be made without grooves on the face. Printed, 6d. Drawings.
February 20, 1807
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 3.571/1812 John Scambler
Improvements in the manufacturing of needles
June 2, 1812
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 4.627/1821 James Winter
Machine for sewing, &c, leather gloves
Improvements in the apparatus for sewing and pointing leather gloves described in the Specification of Letters Patent, dated February 20, 1807, GB 3.012. In this instance the jaws which hold the leather, instead of opening and closing by a circular movement upon a joint, are made to open and shut by a parallel horizontal movement, effected by a slider and screw. The "indexes" for guiding the needles are connected to the upper part of the jaws by screws passing through elongated holes, which render them capable of adjustment. Two indexes of improved construction are also described. Printed, 6d. Drawing.
December 19, 1821
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 5.788/1829 Henry Bock
Machinery for embroidering or ornamenting cloths, stuffs and other fabrics
May 2, 1829
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 6.513/1833 Daniel Ledsam and William Jones
Improvements in machinery to be used in the manufacture of pins and needle
November 21, 1833
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 6.931/1835 James Cropper & John Brown Milnes
Improvements in machinery for embroidering and loom machine
1. Machinery for embroidering lace, cloths or other fabrics by means of needles having a point at each end and an eye in the centre; such needles being conducted through the fabric from opposite sides alternately by a spring holder and the position of the fabric being changed from time to time, in order to produce the required form of ornament, by apparatus acting upon the principle of the pentagraph.
2. Improvements in looms whereby the fabrics in course of weaving therein are at the same time embroidered by means of threads supplied from bobbin carriages and which are laid on both the upper and under surfaces of the warp and consequently form additional threads to those which are thrown between the warp threads by the crossing of the shuttle; the threads from the bobbin carriages are laid in such manner as to present an appearance similar to that produced in embroidering with needles by passing ornamenting threads through the fabric. Printed, 2s. 4d. Drawings. A communication from
November 14, 1835
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 7.079/1836 William Sneath
Bobbin Net Machinery
Application of mechanism to bobbin net machinery for the purpose of producing thread-work ornaments on the bobbin net or lace whilst it is being made by the ordinary parts of the bobbin net machinery or such mechanism may be combined into and form a machine independent of and separated from the machinery by which the bobbin net or lace is produced. The instruments used for making each pattern or ornament are, a bent or curved needle, with two eyes, for introducing the ornamenting thread through the lace and leaving a loop thereof; a pair of barbed points or instruments, barbed at opposite sides, for carrying the loop over the place where the needle is next to pass through and a bent hook, by which the ornamenting thread is tied into a knot at the completion of the pattern by dragging one loop through another. Printed, 4s. 2d. Drawings.
May 3, 1836
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 7.228/1836 Gordon Campbell & John Gibson
Improved process or manufacture of silk
both of the city of Glasgow, respectively merchant and throwster, for their invention of a new or improved process or manufacture of silk and silk in combination with certain other fibrous substances; 6 months.
November 19, 1836
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 7.236/1836 William Sneath
Improvements in producing embroidering using Bobbin Net Machinery
1. Producing embroidery or ornaments on muslins, silks and other woven fabrics by applying to such purpose the mechanism referred to in GB 7.079 and also the mode of fastening off each of the ornamenting threads at any determined period by drawing one loop within the other.
2. Apparatus for producing loopwork ornaments on woven fabrics and for fastening off the same by drawing one loop within the other. Hooks and guards are used for making the ornaments on the fabric which is moved vertically or horizontally according to the pattern and the fastening off is performed by the hook which passes the ornamenting loops through the fabric, aided by loop-openers. Printed, 2s. 10d. Drawings.
November 28, 1836
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 7.923/1839 Abel Morrall
Improvements in the making or manufacturing of needles and in the machinery or apparatus employed therein
January 3, 1839
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 8.606/1840 Luke Hebert
Luke Hebert of Birmingham, in the county of Warwick, civil engineer, for his invention of certain improvements in the manufacture of needles; 6 months
August 17, 1840
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 8.948/1841 Edward Newton & Thomas Archbold
A grant unto Edward Newton, of Leicester, manufacturer, and Thomas Archbold, of the same place, machinist, for their invention of improvements in producing ornamental or tambour work in the manufacture of gloves; six months
May 4, 1841
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 10.134/1844 Leonard Bostwick
Machinery for sewing all kinds of cloth or other materials
April 2, 1844
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 10.424/1844 John Fisher & James Gibbons
Manufacture of figured and ornamented lace or net and other fabrics
December 7, 1844
Fisher & Gibbons invented a sewing machine without knowing it.
it was sufficient to invalidate Howe's (or Thomas's) patent, parts of which were accordingly disclaimed.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 10.716/1845 J. Fisher & J. Gibbons and Thomas Roe
Manufacture of lace or net and other fabrics;machinery for figuring or ornamenting lace or net and other fabrics
June 10, 1845
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 11.025/1846 Arthur Eldred Walker
Machinery for sewing
January 6, 1846
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 11.464/1846 William Thomas (Howe' patent)
Machinery for sewing or stitching various fabrics
December 1, 1846
curved needle & shuttle, lockstitch sewing machine
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 12.060/1848 Jean Marie Magnin (Thimonnier' patent)
Machinery for sewing and embroidering
February 9, 1846
barbed or hooked needle, one thread, chain stitch sewing machine
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 12.221/1848 William Thomas (Morey's patent)
Machinery for Sewing and Tambouring
of Cheapside, in the city of London, merchant, for improvements in the manufacture of stays, boots and shoes; also in fastening and connecting fabrics and garments; communicated to me from abroad. 6 months; colonies.
July 26, 1848
needle and hook, one thread, chain stitch sewing machine
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 12.462/1849 Robert Brown
Machinery for perforating, sewing, stitching, pegging and riveting
February 8, 1849
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 12.736/1849 William Thomas & John Marsh
A grant unto William Thomas, of Cheapside, in the city of London, merchant, and John Marsh, foreman to the said William Thomas, for improvements in the manufacture of looped fabrics, stays and other parts of dress; also an apparatus for measuring, being partly a communication; 6 months
August 9, 1849
one thread, beards needles, tambour stitch
-----------------------------------------------------------------
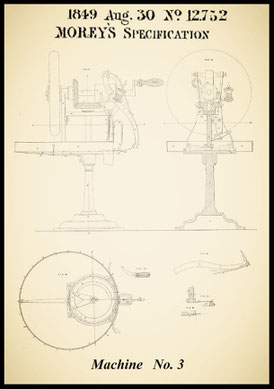
Sewing machinery or apparatus for sewing, embroidering and uniting or ornamenting by stitches, various descriptions of textile fabrics
August 30, 1849
Patent for 5 Machines' improvements
curved needle & curved shuttle, lock stitch, rotary machine (No. 3)
curved needle & shuttle, lock stitch, vibrating shuttle, machine (No.4)
US 6.766 Blodgett & Lerow October 2, 1849
Rotary Sewing Machine
US 7.776 Wilson, Allen B. Nov. 12, 1850
Vibrating Shuttle Machine
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 12.842/1849 Robert Parnall
A grant unto Robert Parnall, of the city of London, clothier, for his invention of a new instrument for facilitating the stitching or sewing of woven fabrics; 6 months
November 13, 1849
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 13.038/1850 Robert Reid
A grant unto Robert Reid, of Glasgow, in the county of Lanark, manufacturer, for his invention of certain improvements in weaving; 6 months; colonies
April 15, 1850
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 13.321/1850 J. A. Lerow (Blodgett' patent)
Sewing machine
November 7, 1850
grooved needle & curved shuttle, rotary machine
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 13.325/1850 David Christie
Machinery or apparatus for sewing
November 7, 1850
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 13.494/1851 Frederick R. Robinson
Sewing machine
February 7, 1851
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 13.889/1851 Francis Hastings Greenstreet
of Albany Street, Mornington Crescent, in the county of Middlesex, for improvements in coating and ornamenting zinc; a communication; 6 months.
December 31, 1851
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 13.890/1852 Charles Dickson Archibald
of Portland Place, in the county of Middlesex, esquire, for improvements in the manufacture of bricks and other articles made of plastic materials and in cutting, shaping and dressing the same, as also stone, wood and metals and in the machinery and apparatus employed therein; 6 months; a communication; colonies.
January 8, 1852
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 14.161/1852 Henry Houldsworth
of Manchester, in the county of Lancaster, cotton spinner, for his invention of improvements in embroidering machines and in apparatus used in connection therewith; 6 months
June 10, 1852
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 14.240/1852 Henry Houldsworth and James Houldsworth
both of Manchester, in the county of Lancaster, silk manufacturers, for their invention of certain improvements in the fixing, extending and holding of cloth to receive embroidery and in apparatus applicable thereto; 6 months
July 27, 1852
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 14.256/1852 Edward Joseph Hughes (Judkins' patent)
Machinery for stitching, either plain or ornamentally
August 10, 1852
...Charles Tiot Judkins, an American located in Manchester who was the proprietor of the patent taken out by Edward Joseph Hughes, August 10, 1852, and which included in its specification the machines known in America as the Grover & Baker and the Singer Manufacturing or No. 2 machine. To the former was given the name of the " Lancashire " and it is known by it to this day...
William Newton Wilson (Jan. 1892)
Patent for 3 Machines' improvements
Three legs, two needles, two threads, double loop or double chain stitch or Grover&Baker stitch, vertical or up and down motion feeding (No.1)
Needle & shuttle, lock stitch sewing machine (No.2)

Machine 1
Three legs
Two needles, two threads, double loop or double chain stitch or Grover & Baker stitch, vertical or up and down motion feeding
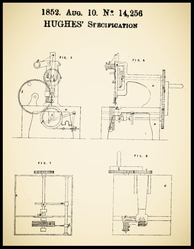
Machine 2
Needle & shuttle, lock stitch sewing machine
In April 1, 1859, a Disclaimer was signed, sealed and delivered by Alexander Stewart Jordan. The Disclaimer and Memorandum of Alteration of certain parts of the Specification and Title, was enrolled in February 9, 1859.
And whereas by divers assignments and finally by an indenture bearing date on or about the January 20. 1858 made between William Emerson Baker of one part and me Alexander Stewart Jordan, of the other part, the said letters patent and Invention and all and singular the rights and privileges thereby granted, became and are now absolutely vested in me.
And whereas the machinery or apparatus for stitching or sewing described in the Specification and shown in the Drawings, Figures 5 to 8 and 20 to 28 inclusive, have not come advantageously into use, I the said Alexander Stewart Jordan, for this reason wish to disclaim and I do hereby disclaim all parts of this Invention.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 14.328/1852 William Edward Newton (Grover&Baker' patent)
Machinery or apparatus for sewing double-looped stitches.
October 19, 1852
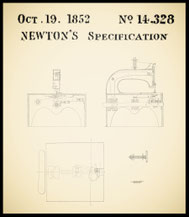
Four legs
Two needles, two threads, double loop or double chain stitch or Grover & Baker stitch, vertical or up and down motion feeding
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 14.359/1853 Bennet Woodcroft
A grant unto Bennet Woodcroft, formerly of Mumps, in the township of Oldham, in the county of Lancaster, but now of Furnival's Inn, in the city of London, gentleman, of an extension for the term of seven years from the fourth day of January 1852, of Letters Patent granted to him and bearing date at Westminster the fourth day of January 1838, for his invention of improvements in the construction of looms for weaving various sorts of cloth, which looms may be set in motion by any adequate power.
July 26, 1853
Note.—Re Campbell and Gibson's Patent.—1836, November 19th. No. 7228.
"A new or improved process or manufacture of silk and silk in combination with certain other fibrous substances"
This Patent, though prolonged for six years, has not yet been re-sealed.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
British Patent GB 14.359/1853 is the last patent granted under the medieval system before the introduction of the Patent Law Amendment Act 1852 on 1 October of that year.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Chronological List of British Patent Models
From March 1617 to July 1853 (Old Series)
GB 1/1730 Aaron Rapburne & Roger Burges March 2, 1617
GB 515/1730 John Kay May 8, 1730
GB 542/1733 John Kay May 26, 1733
GB 701/1755 Charles Frederick Wiesenthal June 24, 1755
GB 955/1770 Robert Alsop March 22, 1770
GB 1.097/1775 William Sheward June 10, 1775
GB 1.764/1790 Thomas Saint July 17, 1780
GB 2.769/1804 John Duncan May 30, 1804
GB 3.012/1807 James Winter February 20, 1807
GB 3.571/1812 John Scambler June 2, 1812
GB 4.627/1821 James Winter December 19, 1821
GB 5.788/1829 Henry Bock May 2, 1829
GB 6.513/1833 Daniel Ledsam and William Jones Nov. 21, 1833
GB 6.931/1835 James Cropper & John Brown Milnes Nov. 14, 1835
GB 7.079/1836 William Sneath May 3, 1836
GB 7.228/1836 Gordon Campbell & John Gibson November 19, 1836
GB 7.236/1836 William Sneath November 28, 1836
GB 7.923/1839 Abel Morrall January 3, 1839
GB 8.606/1840 Luke Hebert August 17, 1840
GB 8.948/1841 Edward Newton & Thomas Archbold May 4, 1841
GB 10.134/1844 Leonard Bostwick April 2, 1844
GB 10.424/1844 John Fisher & James Gibbons December 7, 1844
GB 10.716/1845 J. Fisher & J. Gibbons & Thomas Roe June 10, 1845
GB 11.025/1846 Arthur Eldred Walker January 6, 1846
GB 11.464/1846 William Thomas (Howe) December 1, 1846
GB 12.060/1848 Jean Marie Magnin (Thimonnier) February 9, 1846
GB 12.221/1848 William Thomas (Morey's patent) July 26, 1848
GB 12.462/1849 Robert Brown February 8, 1849
GB 12.736/1849 William Thomas & John Marsh August 9, 1849
GB 12.752/1849 Charles Morey August 30, 1849
GB 14.161/1852 Henry Houldsworth June 10, 1852
GB 14.240/1852 H. Houldsworth & J. Houldsworth July 27, 1852
GB 14.256/1852 E.J. Hughes Charles Tiot Judkins August 10, 1852
GB 14.287/1852 Julian Bernard September 10, 1852
GB 14.314/1852 P. A. Le Comte de Fontaine Moreau October 7, 1852
GB 14.315/1852 Solomon Andrews October 7, 1852
GB 14.316/1852 Alexander Shairp October 7, 1852
GB 14.317/1852 Richard Archibald Brooman October 7, 1852
GB 14.318/1852 Richard Archibald Brooman October 7, 1852
GB 14.319/1852 John Reed Randell October 7, 1852
GB 14.320/1852 William Edward Newton October 11, 1852
GB 14.321/1852 Richard Archibald Brooman October 14, 1852
GB 14.322/1852 Walter Ricardo October 14, 1852
GB 14.323/1852 Thomas Carter October 14, 1852
GB 14.324/1852 John Field October 14, 1852
GB 14.325/1852 William Brown October 18, 1852
GB 14.326/1852 Alfred Vincent Newton October 19, 1852
GB 14.327/1852 Joseph Palin & R. Wm. Sievier October 19, 1852
GB 14.328/1852 William Edward Newton October 19, 1852
GB 14.329/1852 William Edward Newton October 19, 1852
GB 14.330/1852 Edward Henry Jackson October 21, 1852
GB 14.331/1852 Edward Brailsford Bright October 21, 1852
GB 14.332/1852 William Reid October 21, 1852
GB 14.333/1852 William Boggett October 21, 1852
GB 14.334/1852 John Charles Wilson October 21, 1852
GB 14.335/1852 Robert Mcgavin October 23, 1852
GB 14.336/1852 Henry Needham Scrope Shrapnel October 23, 1852
GB 14.337/1852 James Lamb October 23, 1852
GB 14.338/1852 Joseph Walker November 2, 1852
GB 14.339/1852 Patrick McAnaspie November 2, 1852
GB 14.340/1852 John Crowther November 2, 1852
GB 14.341/1852 Louis Arnier November 6, 1852
GB 14.342/1852 P. A. Le Comte De Fontaine Moreau Nov. 6, 1852
GB 14.343/1852 Charles Liddell November 11, 1852
GB 14.344/1852 John Weems November 11, 1852
GB 14.345/1852 Andrew Fulton November 11, 1852
GB 14.346/1852 William Petrie November 13, 1852
GB 14.347/1852 A. E. L. Bellford November 25, 1852
GB 14.348/1852 Moses Poole November 27, 1852
GB 14.349/1852 Lewis Pocock November 27, 1852
GB 14.350/1852 Pierre Jules Lamaille December 1, 1852
GB 14.351/1852 William Gorman December 8, 1852
GB 14.352/1852 George Shaw December 17, 1852
GB 14.353/1852 Robert Burn December 21, 1852
GB 14.354/1852 Robert Galloway December 21, 1852
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 14.354 Last Patent Old Series in 1852
-----------------------------------------------------------------
GB 14.355/1853 Thomas Fildes Cocker January 11, 1853
GB 14.356/1853 Pierre Isidor David February 5, 1853
GB 14.357/1853 Mary Honiball J. Honiball (W. H. Porter) Feb. 9, 1853
GB 14.358/1853 Joseph Gibbs March 21, 1853
GB 14.359/1853 Bennet Woodcroft July 26, 1853
British Patent GB 14.359/1853 is the last patent granted under the medieval system before the introduction of the Patent Law Amendment Act 1852 on 1 October of that year.